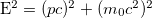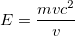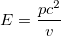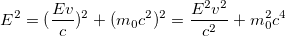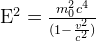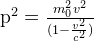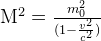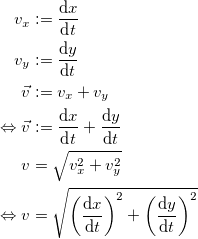- Posts: 2014
speed of light
Now classical speed, or Galilean velocity if you will is indeed relative. It is an approximation of the motions at speeds far below the speed of light. As things move faster, i.e. closer to the speed of light however we find that those models are too simplistic and increasingly fail to describe and predict observations. In the early twentieth century this was mostly theoretical and was hard to observe so it followed from other laws that were in turn easily observable. Now, with particle accelerators, we can actually induce high velocities and observe the resulting behaviour of mass. Now since I didn't thoroughly cover relativity myself, I shan't start with those and then deduce relativistic equations from them.
Now there is the so-called energy-momentum relation, an equation that relates any object's rest mass m0, momentum p and total energy E:
where c is the speed of light.
Since the rest mass of a light quantum (and I mean any electromagnetic quantum, of course) is zero, you can see that the energy of a photon reduces to E=pc and since a massive object at rest has zero momentum (because in that case p=m0v where v is the object's velocity), its energy at rest reduces to E=m0c2.
Now, we can trivially expand the latter equation by v/v=1 resulting in
and with mv=p
Now we solve for pc and feed that into our initial equation to get
Solving for E2 we get
As you can see, as v approaches c, the denominator approaches zero and therefore the total energy E of that object approaches infinity. In other words, the faster you go, the more energy it takes to accelerate any further.
As for the change of mass, we come for the momentum p, twisting the variables we have so far around a bit, to
And since p=Mv where M is the total mass of the object, this reduces to
As you can see, the total mass of an object not only doesn't decrease with increasing velocity, but indeed, the opposite is the case: As a massive body accelerates approaching light speed, it actually quite rapidly gains mass, which explains why it gets increasingly impossible to accelerate it further the faster it already moves.
I would like to stress that I am very much a layman at this point. While the conclusions, as far as I know, are correct, I presume that my ways of getting to them that I presented here may be severely flawed in several places. Bearing that in mind I hope it was still marginally helpful.
Better to leave questions unanswered than answers unquestioned
Please Log in to join the conversation.
- OB1Shinobi
-
 Topic Author
Topic Author
- Offline
- Banned
-
Inactive
- Posts: 4394
i wonder if traveling backwards in time would cause mass to transform into light
if mass gains mass as it picks up speed the only thing i can think of as the opposite of speed is reverse time
i may not be much of a scientist but im a pretty good story teller lol
it bothers me that speed of light is not possible
what if i build a machine which turns a cylinder to produce energy
the cylinder is originally turned through nomal magnet power but its got electro magnets attached also
the produced energy is stored into a capaciter or a battery
or something - every time a certain amount of energy is stored; let.me call it just call it 10
whenever 10 is stored 1 gets fed back into the spin of the cylinder by being directed to the electro magnets
the idea being that the more power used to turn the cylinder the faster it goes - every time it reaches the next 10 it puts another 1 back into the system making the cylinder spin just a little faster
unless it explodes its an infinitie progression - doesnt it HAVE to reach the speed of light eventually?
People are complicated.
Please Log in to join the conversation.
KSP Special Relativity ( 1 of 9 ) Introduction : http://youtu.be/KKAwpEetJ-Q
A little song that I like (interlude)
Shall we gather at the river? : http://youtu.be/Qca8B5NbX5Y
Others video on relativity
Albert Einstein's Theory of Relativity : http://youtu.be/ev9zrt__lec
Relativity and Time Dilation : http://youtu.be/aZrjMmMBa_8
Don't contest the light....
Simple Relativity - Understanding Einstein's Spec… : http://youtu.be/TgH9KXEQ0YU
Please Log in to join the conversation.
Positrons are sometimes thought of as electrons traveling back through time. They still have mass and are still not quite the same as a light particle... Then again, with only one direction of time available to our observation as of now, it is difficult to say. I wouldn't know why mass moving back in time should suddenly lose its mass. In fact, if its energy stay constant, then that'd mean it would have to gain momentum and why that would happen is also currently beyond me. In any case, numerous reactions, most prominently nuclear fusion and fission, operate on the equivalence of mass and energy. When you burn a piece of paper and you conserve the smoke and the ash, the total mass of the system will in fact decrease and the light and heat the flames emitted amount to just that difference.OB1Shinobi wrote: i wonder if traveling backwards in time would cause mass to transform into light
Speed is defined as the euclidian norm of velocity. Let x and y be arbitrary linear independant directions, forming a two-dimensional vector space. Let t be time, vector v be velocity and v be speed.if mass gains mass as it picks up speed the only thing i can think of as the opposite of speed is reverse time
Now, even with t being negative, indicating 'reverse time', if you will, since it is in every instance being raised to the second power, the entire expression can never be negative. Speed is always either zero or positive.
You would win more than just the Nobel Prize. Before you get too hopeful though, bear in mind that such a device would violate the first law of thermodynamics and patent offices grew so tired of people trying that many have special policies on machines with that ambition.what if i build a machine which turns a cylinder to produce energy
It could be originally set in motion by a user or by a convenient assymmetrical configuration of electromagnets. You are describing an electromotor right now.the cylinder is originally turned through nomal magnet power but its got electro magnets attached also
So you are saying that for every one unit of energy it gets it puts out ten? Essentially what you are describing is an electric generator, which is a reverse electric motor, if you will, but this one not only doesn't lose any energy to friction, it somehow produces energy out of thin air. Where do the additional nine units come from?the produced energy is stored into a capaciter or a battery or something
every time a certain amount of energy is stored; let.me call it just call it 10
whenever 10 is stored 1 gets fed back into the spin of the cylinder by being directed to the electro magnets
Unless your machine is made out of light rather than matter, it will have a rest mass. If it has a size, that mass will also not be located on the rotation axis but actually somewhere where it will experience motion. And as by the formula above, so long as the rest mass is not zero, with increasing speed, total mass will, again, increase ad infinitum. So even if we had a motor that we would feed more and more energy into the device, as long as we only have finite energy at our disposal, no part of it will get to light speed, eventhough we can get very close indeed. If we did have a self-sustaining device that could actually conjure up energy out of nowhere, until it reached light speed, literally infinite time would have to pass, because in a finite time only a finite amount of energy would be generated. The only way to get massive objects to light speed is to conjure up infinite energy in an instant.the idea being that the more power used to turn the cylinder the faster it goes - every time it reaches the next 10 it puts another 1 back into the system making the cylinder spin just a little faster
unless it explodes its an infinitie progression - doesnt it HAVE to reach the speed of light eventually?
Better to leave questions unanswered than answers unquestioned
Please Log in to join the conversation.
- OB1Shinobi
-
 Topic Author
Topic Author
- Offline
- Banned
-
Inactive
- Posts: 4394
yes it could initially be set in motion by a light touch
actually even that wouldnt ve necessary i think
generally speaking its my thought that the basic dynamo concept could be applied to every hinge and sliding surface in a home which would mean that every time someone opened their refrigerator or cupboard or any door in the house they would generate a small charge of elecetricity which would be stored in a central battery or whatever the appropriate storage device may be
the dynamo was an elaboration on this concept so that the energy didnt have to be produced manually
if a dynamo is light enough at its fulcrum (ive found that others have thought of this part - there are magnetic fan blade dynamos on youtube) to be rotated by the influence of the normal magnets
but it also has electric magnets ready to add to the amount of magnetic pressure applied to the rotation of the cylinder or the fan blades (which was how i originally thought of it too) the the first thing the dynamo does is to create energy
this energy is stored until it reaches 10 points
the 11th point of energy is applied to the electric magnets
this cycle is repeated
also the 1-10 ratio is completely arbitrary
its probably not the most apporopriate ratio for either energy production for a home or for reaching light speed -though i guess im letting go of that ambition for the time. the point was free clean energy and this device would do that if my assumption about our technological ability to store measure and reapply electric energy and my understanding of electric magnets are both accurate
People are complicated.
Please Log in to join the conversation.
Self Org. Systhems Vector Equilibrium Flower Of… : http://youtu.be/9n-vb71VZzk
Free Energy and the Equilibrium Constant : http://youtu.be/F1k8TJsVg_g
Einstein on faster-than-light speeds? : http://youtu.be/l9aLyfFnfOU
And nano carbon? It's military sciences. They are not giving the tech even if we need it to make plasma lightsaber... We are going need to do it with telekinesis.
There are some stone that have rubidium. Thats substance in gaz are the one who make the light with mass. Right now they are using this Tech for make quantum computer. A rubidium onze cost much more than gold.
Please Log in to join the conversation.
The sun is the most free energy source at our disposal. To harvest it either directly or through biomatter is as close as we can get to free energy. And plenty at that, if we go as far as building a dyson sphere around it, but there will not come a machine that conjures up energy out of nothing unless it runs on magic. That's not a matter of technology either. That's just the universe we have to deal with for it is the one we've been dealt.
Better to leave questions unanswered than answers unquestioned
Please Log in to join the conversation.
Please Log in to join the conversation.
Through passion I gain strength and knowledge
Through strength and knowledge I gain victory
Through victory I gain peace and harmony
Through peace and harmony my chains are broken
There is no death, there is the force and it shall free me
Quotes:
Out of darkness, he brings light. Out of hatred, love. Out of dishonor, honor-james allen-
He who has conquered doubt and fear has conquered failure-james allen-
The sword is the key to heaven and hell-Mahomet-
The best won victory is that obtained without shedding blood-Count Katsu-
All men's souls are immortal, only the souls of the righteous are immortal and divine -Socrates-
I'm the best at what I do, what I do ain't pretty-wolverine
J.L.Lawson,Master Knight, M.div, Eastern Studies S.I.G. Advisor (Formerly Known as the Buddhist Rite)
Former Masters: GM Kana Seiko Haruki , Br.John
Current Apprentices: Baru
Former Apprentices:Adhara(knight), Zenchi (knight)
Please Log in to join the conversation.
- OB1Shinobi
-
 Topic Author
Topic Author
- Offline
- Banned
-
Inactive
- Posts: 4394
this video proves that im on to SOMETHING - not that im right per se but that i am generally interpreting the relationship between light and time in a functional way
im going to spend a good bit of time on these and other related videos
this is an awesome thread
thanks to everybody
keep it coming!
People are complicated.
Please Log in to join the conversation.